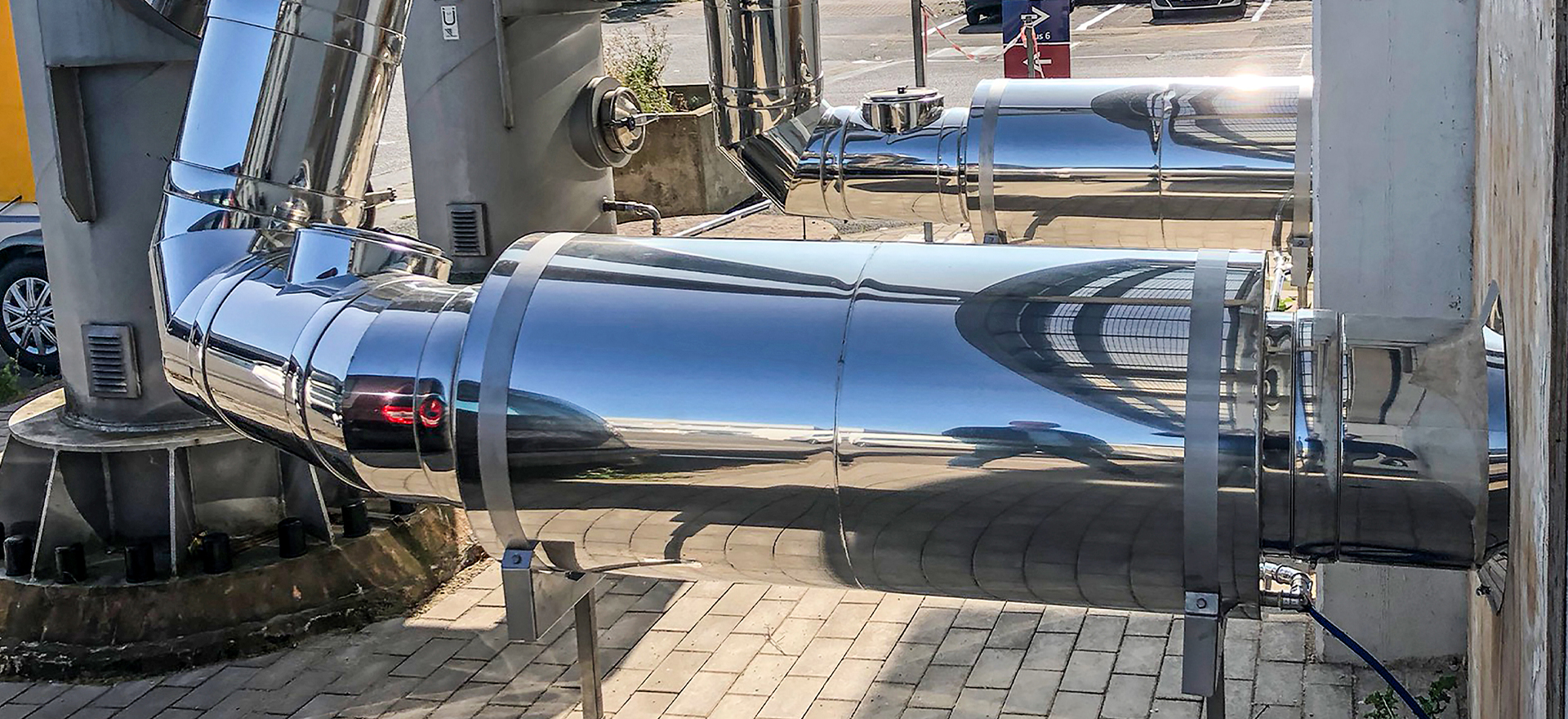
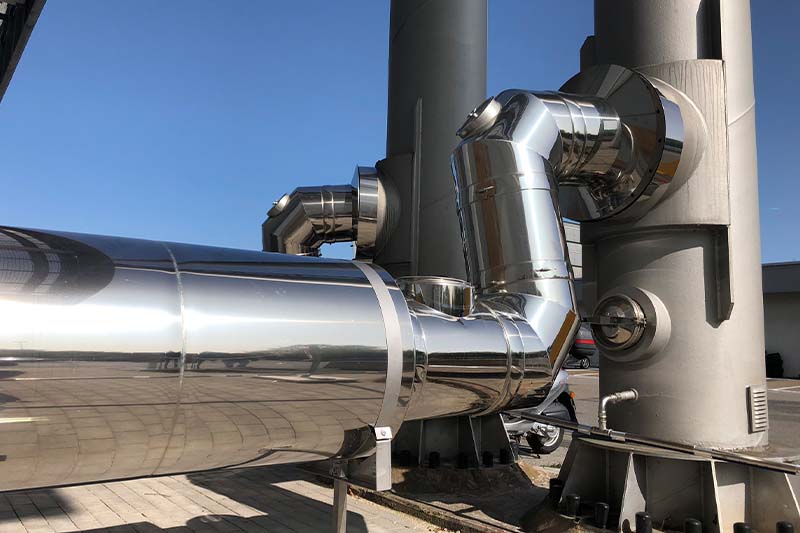
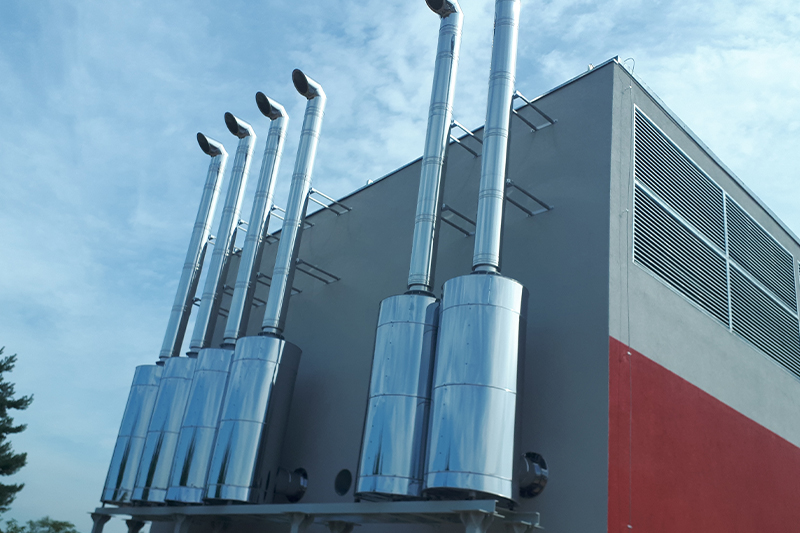
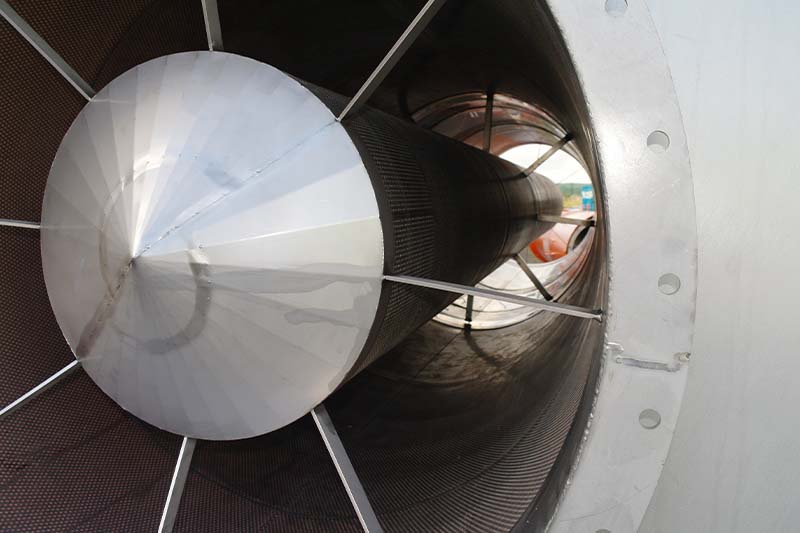
Exhaust silencer
| Frequency range | silencer type | silencer series for | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| boiler | chp | biomass | ||
| predominantly medium and high frequency | absorption silencer | ASD | AED | AVD |
| predominantly low frequency | reflection / resonance silencer | RSD | RED | |
| broadband frequency frange | combined silencer | KSD | KED | |
boiler
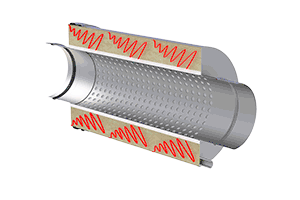
The exhaust gases produced during the combustion process are released into the environment via the exhaust system. Here, flame noises from the boiler room as well as the “whirring” of the fan installed in condensing boilers can be transmitted. As a rule, these are medium and high-frequency noises that can be reduced using an absorption silencer. Especially with newer forced-air burners, the use of a combined silencer or a pure resonance silencer may be necessary for a broader range of damping.
combined heat and power plant / generators
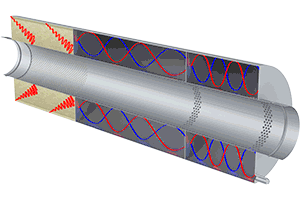
In combined heat and power plants and generators, a motor primarily generates electrical power, with additional usable heat being generated in the CHP plant. The engine noise is often noticeable as a low-frequency hum; the individual frequency spectrum and thus the selection of the appropriate type of silencer depend to a large extent on the number of cylinders and the speed of the engine.
Biomass boiler
The combustion of biomass such as wood, pellets or wood chips is almost silent. In this case, integrated fans are solely responsible for annoying, mostly medium to high-frequency noises. Due to the more aggressive composition of the exhaust gases, it is advisable to use an adapted absorption silencer with resistant glass silk fabric for biomass boilers.